Sleep apnea diagnosis and treatment
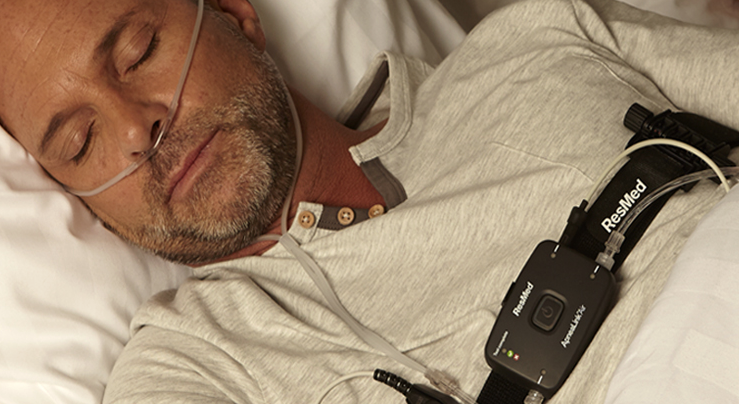

diagnostic test
1,A level 1 sleep test also called a Polysomnography (PSG) 2,A home sleep apnea test (HSAT)
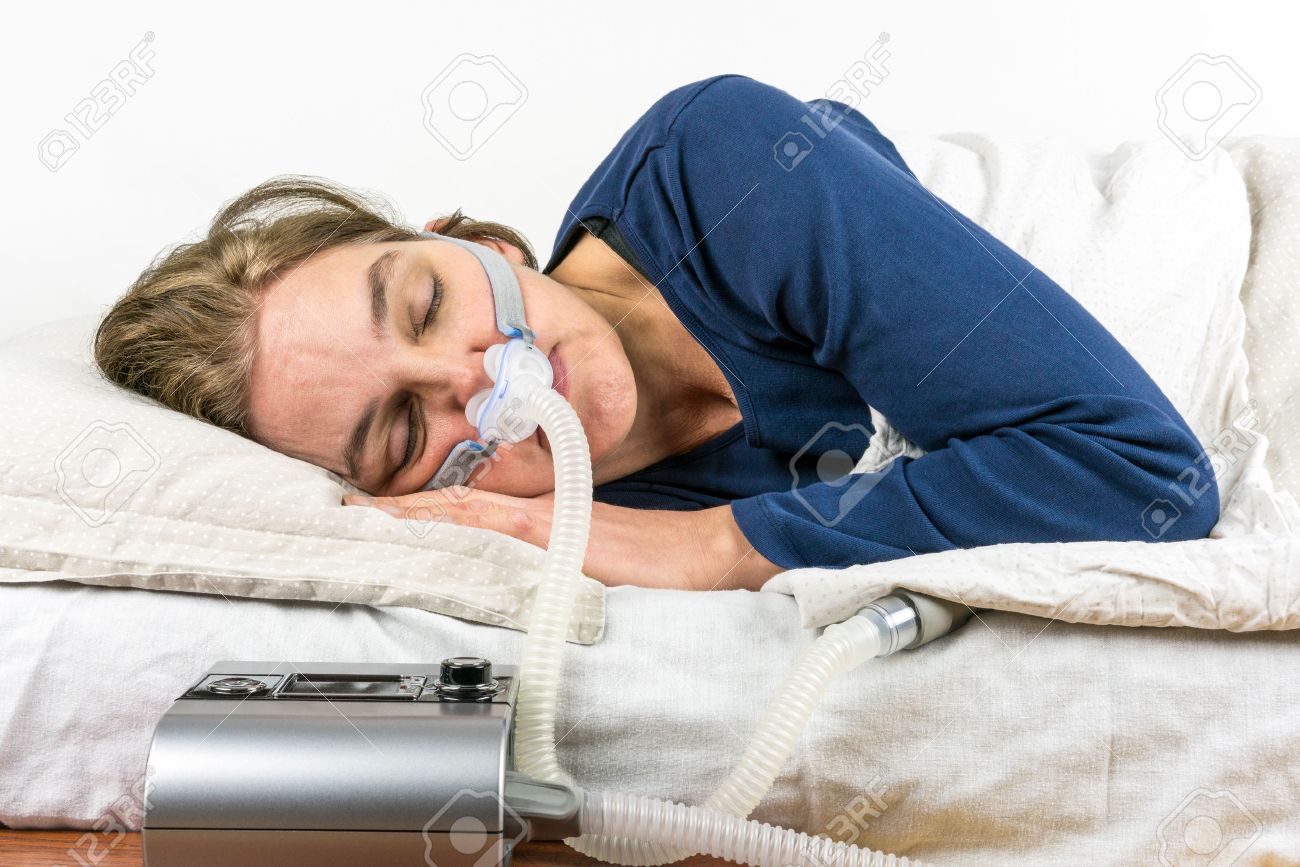
CPAP TREATMENT
Fuerat aestu carentem habentia spectent tonitrua mutastis locavit liberioris inistra possedit.
wHAT IS SLEEP APNEA?
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing throughout the sleep cycle.
FAQ
Most frequent questions and answers
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder that occurs when a person stops breathing or has pauses in their breathing during sleep. These breathing interruptions are caused when there is a partial or complete collapse of the upper airway or throat during sleep. These breathing pauses can last from a few seconds to minutes and may occur 30 times or more an hour! Anyone who stops breathing 30 times or more an hour likely has severe sleep apnea. And the brain and the body may not get enough oxygen. Sometimes after a breathing pause, a loud snort or choking sound can be heard when the body returns to normal breathing. And if you have a bed partner they may complain of your loud snoring which is often a sign of sleep apnea.
- Loud irregular snoring
- Gasping or choking during sleep
- Exhaustion and always feeling tired
- Poor concentration
- Lack of energy
- Forgetfulness
- Frequent urination at night
- Leg cramps
- Weight gain
- Sexual dysfunction
- Depression or anxiety
- Reduced enjoyment of life
- Extra tissue in the back of the airway such as large tonsils
- Decrease in the tone of the muscles holding the airway open
- The tongue falling back and closing off the airway
- Abnormal anatomy such as a recessed jaw
A Home Sleep Apnea Test (HSAT) is a test that uses a small portable sleep recorder to be worn overnight while you sleep in the comfort of your own home. The portable home sleep recorder will record your oxygen levels, your breathing, your heart rate, chest movements and show if you were snoring and what position you slept in. The results of an overnight Home Sleep Apnea Test will be interpreted by a board-certified sleep physician to diagnose sleep apnea.
Ask your doctor to schedule a In-Lab Sleep Lab Study. RHS can also assist with a referral to a Sleep Lab Study
Sleep apnea, like many other disorders comes in varying degrees of severity and occurs for various reasons. To effectively treat all patients with sleep apnea there are many different therapeutic options. These include:
- Lifestyle changes
- Body positioning
- Dental appliances
- Surgery
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
LIFESTYLE CHANGE Many of the lifestyle changes that improve OSA will also improve one’s overall health. Lifestyle changes are often the hardest things to accomplish, but perseverance can make a dramatic improvement in people with OSA. Regardless of the final treatment or treatments chosen, the items described below are worthwhile goals.
OBESITY Obstructive sleep apnea is often associated with obesity. Overweight individuals often have respiratory problems due to thick chest walls and increased compression on the diaphragm from abdominal contents. The thick neck often seen in obesity also increases airway resistance. Weight loss, even in small amounts, can therefore have a profound effect on improving sleep apnea.
ALCOHOL Alcohol when consumed in excess can exacerbate snoring and OSA. The muscles of the upper airway have been shown to loose muscle tone after consumption of even a small amount of alcohol. Individuals with sleep apnea should avoid alcohol 4-6 hours before bedtime. interested in quitting smoking, talk to your family physician or one of our respiratory therapists.
MEDICATIONS As with alcohol, certain medications like narcotic pain relievers and barbituates often worsen OSA. Talk with your physician to decide if you are currently taking any medications that should be avoided.
CPAP, which stands for Continuous Positive Airway Pressure is a specific pressure-generating machine that provides air pressure to a mask worn on your nose or mouth. The pressure generated within this mask is applied to your airways and lungs. This applied pressure acts like a splint, keeping the airway patent and free of snoring and obstruction. CPAP is 99% effective when used appropriately and is considered the GOLD STANDARD.
Long-term suffering of sleep apnea causes serious health conditions such as high blood pressure, heart attacks, coronary artery disease and stroke. Also, there is strong correlation between untreated sleep apnea and Type 2 Diabetes. Sleep apnea sufferers can experience an increase in daytime sleepiness which can cause irritability, depression and memory problems. Daytime sleepiness contributes to lack of concentration and falling asleep during the day. This impacts quality of life and can also significantly increase the risk of industrial and automotive accidents.
SLEEP HYGIENE: The following is a brief list of general tips to promoting a better night’s sleep:
- Establish a regular routine that includes going to bed and getting up at the same time every day, even on weekends. Regular sleep is key to better health overall.
- Do not nap during the day as this results in poor sleep at night.
- Go to bed when you are sleepy. If you have difficulty falling asleep or wake up shortly after going to sleep, leave the bedroom and read quietly or do some other relaxing activity. Avoid overly bright lights as this can cue your wake cycle.
- Develop sleep rituals before going to bed. Do the same things in the same order before going to bed to cue your body to slow down and relax.
- Avoid stress and worries at bedtime. Address tomorrow’s activities, concerns, or distractions earlier in the day. Certain activities, such as listening to soft music, reading, or taking a warm bath, can help you wind down.
- Use your bed for sleeping only. Often, doing other activities in bed like watching TV, paying bills, or working only serve to initiate worries and concerns. Let your mind associate the bed with sleeping and relaxing.
- Avoid heavy meals late in the evening; similarly, avoid going to bed hungry. A light snack, especially dairy foods, can help you sleep.
- Reduce your intake of caffeine and nicotine 4-6 hours before going to sleep. Stimulants interfere with your ability to fall asleep and progress into deep sleep.
- Exercise regularly. Regular exercise, even for 20 minutes, 3 times a week, promotes deep sleep. Avoid exercise in the evening within 3 hours of bedtime.
- Don’t nap for more than 30 minutes or after 3 p.m. Avoiding naps all together will ensure that you are tired at night. Longer naps disrupt the body’s ability to stay asleep.
- Maintain a dark, quiet, and cool room for sleep.
Snoring and OSA are usually worse when you sleep on your back. This is because gravity promotes collapse of the soft palate and the tongue, especially during deep sleep when the muscles are most relaxed. There are several body positioning strategies that can help you if you have mild apnea only when lying on your back. Some patients sew a tennis ball or marble into the back of their pajamas to train themselves to sleep on their sides. Another technique is to use positional pillows to assist you in sleeping on your side. For some patients who are very overweight, sleeping with their torso elevated 30 degrees relieves the pressure on the diaphragm (from the abdomen) and improves patency of the upper airway. Positional techniques have their limits, but many have been tried with success.
